Secant pile walls are formed by constructing intersecting reinforced concrete piles. The piles are reinforced with either steel rebar or with steel beams and are constructed by either drilling under mud or augering. Primary piles are installed first with secondary piles constructed in between primary piles once the latter gain sufficient strength. Pile overlap is typically in the order of 3 inches (8 cm). In a tangent pile wall, there is no pile overlap as the piles are constructed flush to each other. The main advantages of secant or tangent pile walls are:
1. Increased construction alignment flexibility.
2. Increased wall stiffness compared to sheet piles.
3. Can be installed in difficult ground (cobbles/boulders).
4. Less noisy construction.
The main disadvantages of secant pile walls are:
1. Verticality tolerances may be hard to achieve for deep piles.
2. Total waterproofing is very difficult to obtain in joints.
3. Increased cost compared to sheet pile walls.
Secant pile wall design when steel beams are used involves the use of weaker than normal concrete. The pile that is lagging the wall between two main beams has to be examined for shear and compression arching.
Secant pile walls can be used for temporary support of deep excavations or to form permanent earth retention systems. They can also serve the dual function of excavation support during construction and as part of the permanent foundation system. Since secant pile installation creates minimal disturbance, this technique is suited for dense, urban environments. Walls are constructed by the sequenced construction of overlapping, reinforced concrete piles installed in a top-down process by either drilling or augering methods. Although more costly than sheeted excavation support, this system offers greater alignment flexibility and increased wall stiffness and can be installed through bouldery or cobbly soils.
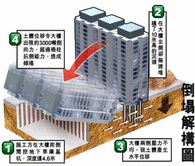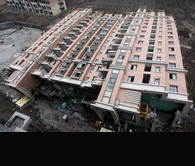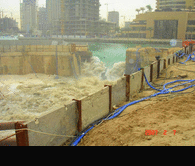
Secant pile wall construction is the most economical method of creating an effective water control barrier for dam remediation. Drilling techniques are used to construct overlapping concrete elements through rock, extending below the water seepage elevation. Sequenced drilling and concreting of the individual elements that make up the finished barrier allows the concrete to cure, ensuring a tight seal between elements for complete water cut off. Secant Pile Walls can be constructed to depths of 120 ft.
More Information on Basement & Slope Retention
Contiguous pile wall - typical diameters and spacing
| Diameter mm | Spacing mm |
| 350 450 600 750 | 400 600 750 900 |
Secondary hard/soft secant pile wall - typical diameters and spacing
| Diameter mm | Spacing mm | |
| Primary | Secondary | |
| 450 600 750 | 450 600 750 | 600 900 1000 |
Typical applications of embedded retaining walls
(ICE Specification for Piling and Embedded Retaining Walls)
| Wall Type | Typical height range | Groundwater control | Typical vertically | ||
| Cantilever | Propped | Temp. | Perm. | ||
| Sheet pile wall | To 5m | 4 - 15m | Yes | No | 1:75 |
| Combination wall | To 10m | 5 - 20m | Yes | No | n/a |
| King post | To 4m | 4 - 20m | No | No | n/a |
| Contiguous | To 5m | 4 - 20m | No | No | 1:75 |
| Hard/soft secant | To 5m | 4 - 20m1 | Yes2 | No | 1:75 |
| Hard/hard secant | To 6m | 4 - 25m | Yes | Yes | 1:200 |
| Diaphragm wall | To 8m | 5 - 30m | Yes | Yes | 1:75 |
Notes:
1. The depth to which hard/soft pile walls can provide water resistance is restricted by
the construction tolerances of the boring rig and the groundwater pressure to be
resisted. This type of wall is most commonly used to resist groundwater flow to
maximum depths of approximately 6m.
2. The long term resistance of the soft elements of hard/soft secant pile walls to
groundwater flow has not been proven and will vary according to the soft mix design.
It is recommended that long term water resistance is provided for by additional works
such as reinforced concrete lining walls which transfer the groundwater load into the
hard elements.
Tangent Pile Wall
Tangent pile walls are a variation of secant pile walls and soldier pile walls. However, tangent pile walls are constructed with no overlap and ideally one pile touches the other. Compared to secant pile walls, tangent pile walls offer the following advantages:
1. Increased construction alignment flexibility.
2. Easier and quicker construction.
The main disadvantages of tangent pile walls are:
1. They are can not be used in high groundwater tables without dewatering.
2. Each pile is independent from adjacent piles




















 Dollar Amerika tukar, currency converter
Dollar Amerika tukar, currency converter
No comments:
Post a Comment